Let's talk about GS pay scale 2023, folks. If you're working for the federal government or thinking about joining the ranks of Uncle Sam's employees, you've probably been wondering how the salary structure works. The General Schedule (GS) pay scale is like the backbone of government employment, and understanding it can make a world of difference in your career planning. So, grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let's break it down step by step.
Now, why does the GS pay scale matter? Well, it's not just about the money—it's about fairness, transparency, and making sure employees are compensated based on their skills and experience. Whether you're a fresh-faced newbie or a seasoned pro, the GS pay scale is designed to ensure that everyone gets what they deserve. But hey, let's not sugarcoat it: the system can be a little confusing at first glance. That's where we come in!
In this article, we're diving deep into the GS pay scale 2023, covering everything from the basics to the nitty-gritty details. By the time you're done reading, you'll have a solid grasp of how it works, how to calculate your pay, and what factors might affect your salary. So, let's get to it, shall we?
Read also:Vince Gill Net Worth Exploring The Wealth Behind The Country Music Legend
Table of Contents
- What is the GS Pay Scale?
- GS Pay Scale Structure
- GS Pay Scale 2023 Overview
- How to Calculate GS Pay
- Pay Grades and Steps
- Location-Based Pay Adjustments
- Benefits and Perks Beyond Salary
- Common Misconceptions About GS Pay
- The Future of the GS Pay Scale
- Conclusion: What You Need to Know
What is the GS Pay Scale?
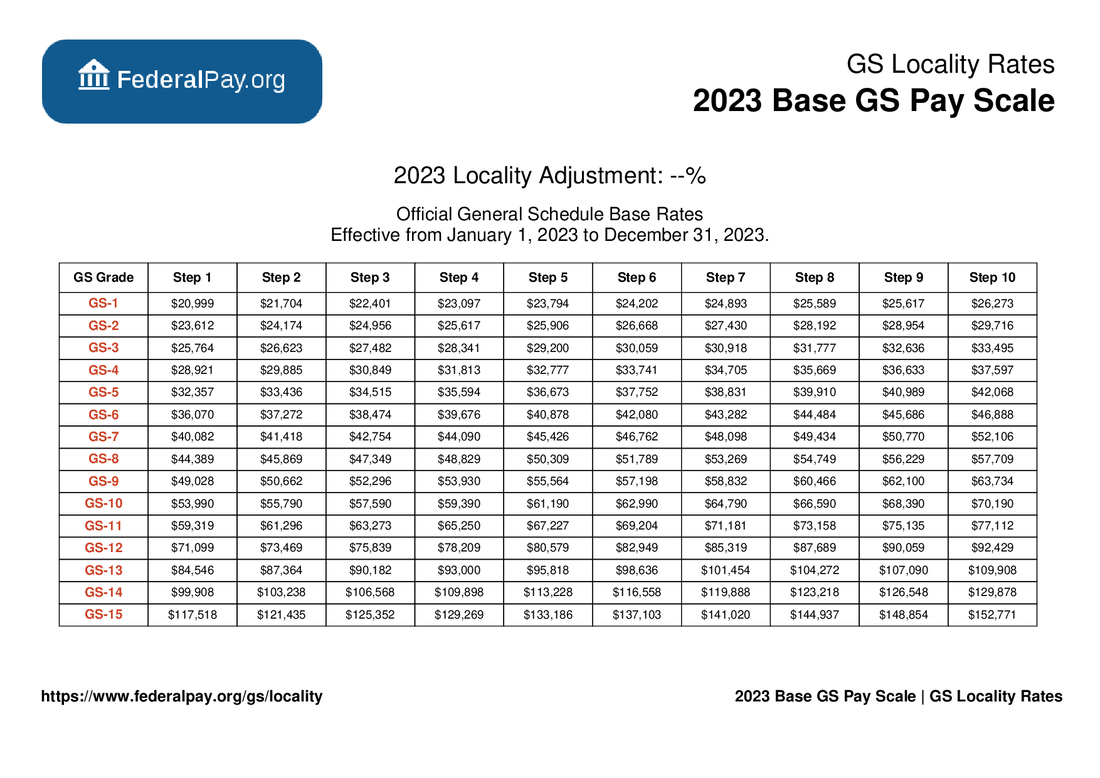
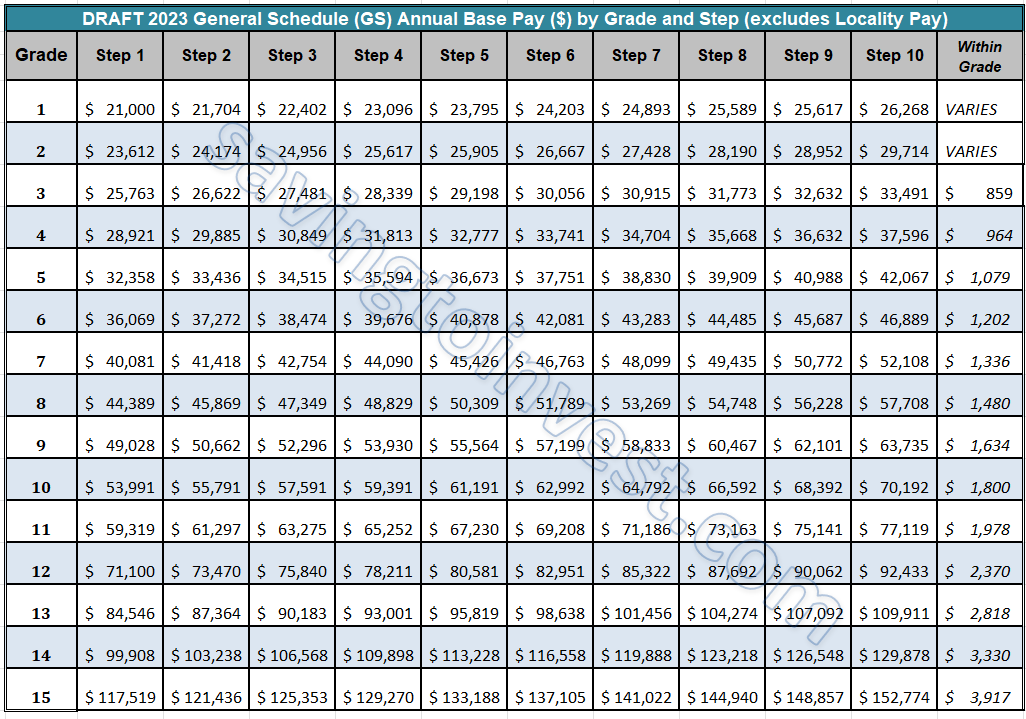
The GS pay scale, short for General Schedule, is the federal government's standardized pay structure for white-collar employees. It's been around since 1949 and has evolved over the years to keep up with inflation, cost of living, and other economic factors. Think of it as a roadmap for determining how much you'll earn based on your job level and location.
Here's the deal: the GS pay scale is divided into grades and steps. There are 15 grades (GS-1 to GS-15), and each grade has 10 steps. As you climb the ladder, both in terms of grade and step, your pay increases. It's a pretty straightforward system, but there are a few twists that we'll get into later.
Who Uses the GS Pay Scale?
Most federal civilian employees fall under the GS pay scale. This includes roles in agencies like the Department of Defense, the FBI, the IRS, and many others. However, not everyone in the federal workforce uses it. Some positions, like senior executives or law enforcement officers, have their own pay systems. But for the majority of government jobs, the GS pay scale is the go-to.
GS Pay Scale Structure
Alright, let's talk structure. The GS pay scale is built around two main components: grades and steps. Each grade represents a level of responsibility, and each step within a grade reflects incremental progress and experience.
- Grades: There are 15 grades in total, starting from GS-1 (entry-level) to GS-15 (senior-level).
- Steps: Each grade has 10 steps, and moving up a step typically results in a small pay bump.
For example, a GS-5 employee at Step 1 earns less than a GS-5 employee at Step 10. It's all about progress and experience. But wait, there's more! Location also plays a big role, which we'll cover in a bit.
How Often Do You Move Up?
Moving up in the GS pay scale isn't automatic. You usually need to meet certain criteria, like time in service or performance evaluations, to advance to the next step. Typically, it takes about one to three years to move up a step, depending on the position and agency policies.
Read also:Hakeem Lyon The Rising Star You Need To Know About
GS Pay Scale 2023 Overview
Now, let's zoom in on the GS pay scale 2023. This year, federal employees received a pay raise to keep up with inflation and other economic factors. The exact percentage varies depending on your location and grade, but the overall increase was around 4.6%. Not bad, right?
Here's a quick breakdown of the base pay for some common grades:
- GS-5: Starting at around $33,000
- GS-7: Starting at around $40,000
- GS-11: Starting at around $60,000
- GS-15: Starting at around $100,000
These numbers are just the base pay, though. Remember, location-based adjustments can significantly impact your final salary.
What's New in 2023?
In 2023, the government introduced some changes to the locality pay system. Instead of having broad regions, they refined the adjustments to better reflect the cost of living in specific areas. This means employees in high-cost cities like San Francisco or New York might see a bigger bump than those in smaller towns.
How to Calculate GS Pay
Calculating your GS pay might sound complicated, but it's actually pretty straightforward once you know the formula. Here's how it works:
Base Pay + Locality Pay = Total Salary
Let's break it down:
- Base Pay: This is the standard rate for your grade and step, as determined by the Office of Personnel Management (OPM).
- Locality Pay: This is an adjustment based on where you live. Some areas, like Washington D.C. or Seattle, have higher costs of living, so the locality pay is higher.
For example, if you're a GS-11 Step 1 employee in San Francisco, your base pay might be $60,000, but with locality pay, it could jump to $80,000 or more. See how that works?
Tools to Help You Calculate
Don't feel like doing the math yourself? No problem! The OPM offers an online calculator that does all the heavy lifting for you. Just plug in your grade, step, and location, and voila—you'll have your estimated salary in seconds.
Pay Grades and Steps
Let's dive deeper into pay grades and steps, because understanding these is key to navigating the GS pay scale.
Pay Grades
As we mentioned earlier, there are 15 pay grades in the GS system. Here's a quick rundown:
- GS-1 to GS-3: Entry-level positions, usually for clerical or support roles.
- GS-4 to GS-6: Mid-level positions, often requiring some education or experience.
- GS-7 to GS-9: Professional roles, typically requiring a bachelor's degree or equivalent experience.
- GS-10 to GS-12: Senior professional roles, often requiring advanced degrees or extensive experience.
- GS-13 to GS-15: Executive or managerial roles, usually requiring significant expertise and leadership skills.
Steps Within Each Grade
Each grade has 10 steps, and moving up a step usually results in a 3% to 15% pay increase, depending on your grade. For example, moving from GS-7 Step 1 to GS-7 Step 2 might give you a 3% bump, while moving from GS-15 Step 9 to GS-15 Step 10 could be closer to 15%.
Location-Based Pay Adjustments
Location, location, location—it's not just important in real estate. Where you live can have a huge impact on your GS pay. The federal government uses something called locality pay to account for differences in cost of living across the country.
Here's how it works: the OPM divides the U.S. into different pay areas, each with its own adjustment percentage. For example, employees in the New York City area might get a 30% locality pay adjustment, while those in rural areas might get only 10%.
How to Find Your Locality Pay
To find your locality pay, check the OPM's official list of pay areas. It's updated annually and includes detailed information on each region's adjustment percentage. You can also use the online calculator we mentioned earlier to get a more precise estimate.
Benefits and Perks Beyond Salary
While the GS pay scale is all about the money, it's not the only perk of working for the federal government. Employees also enjoy a range of benefits that can add significant value to their overall compensation package.
- Health Insurance: Comprehensive plans with affordable premiums.
- Retirement Plans: Generous contributions to your retirement account.
- Paid Time Off: Generous vacation and sick leave policies.
- Flexible Work Schedules: Many agencies offer telework and flexible hours.
These benefits can make a big difference in your quality of life, so don't overlook them when evaluating your total compensation.
Common Misconceptions About GS Pay
There are a few myths floating around about the GS pay scale that we need to clear up. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Myth #1: All federal employees earn the same salary. Reality: Pay varies widely based on grade, step, and location.
- Myth #2: The GS pay scale is stagnant. Reality: It's updated annually to reflect changes in the economy.
- Myth #3: Moving up is automatic. Reality: Advancement requires meeting specific criteria, like time in service and performance evaluations.
Understanding these misconceptions can help you make more informed decisions about your career.
The Future of the GS Pay Scale
Looking ahead, the GS pay scale is likely to continue evolving to keep up with changing economic conditions. Some experts predict that the government may introduce more flexible pay structures to attract top talent in competitive fields. Others think we might see more emphasis on performance-based pay rather than seniority.
Whatever the future holds, one thing is certain: the GS pay scale will remain a key part of federal employment for years to come. So, whether you're just starting out or looking to advance, it's worth staying informed about how it works and how it might change.
Conclusion: What You Need to Know
Alright, folks, that's a wrap on our deep dive into the GS pay scale 2023. Here's a quick recap of what we covered:
- The GS pay scale is the federal government's standardized pay structure for white-collar employees.
- It's divided into grades and steps, with each grade representing a level of responsibility and each step reflecting progress and experience.
- Location-based adjustments play a big role in determining your final salary.
- Benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off add significant value to your overall compensation package.
So, whether you're just starting out or looking to climb the ladder, understanding the GS pay scale can help you make the most of your federal career